https://www.acmicpc.net/problem/15686
15686번: 치킨 배달
크기가 N×N인 도시가 있다. 도시는 1×1크기의 칸으로 나누어져 있다. 도시의 각 칸은 빈 칸, 치킨집, 집 중 하나이다. 도시의 칸은 (r, c)와 같은 형태로 나타내고, r행 c열 또는 위에서부터 r번째 칸
www.acmicpc.net
M개의 치킨집을 골라 도시의 치킨거리 합을 최소로 해야합니다.
인덱스를 이용하여 집의 좌표와 치킨집의 좌표를 각각 저장해놓습니다.
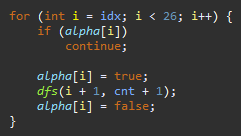
그 다음 모든 가능한 경우를 구해야하기 때문에 조합으로 고른 치킨집의 인덱스를 pick 배열에 저장하여
M개를 골랐으면 집과 고른 치킨집의 거리를 N^2으로 구하였습니다.
고른 인덱스의 다음 인덱스를 재귀로 보내야하는데 계속 실수하는 바람에 시간초과 한번 떴습니다 ㅠㅠ... 왜 매번 이런 실수를 반복하는지..
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
|
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
import java.util.StringTokenizer;
public class Main {
static BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
static StringTokenizer st;
static int list[][], house[][], chicken[][], pick[][];
static int N, M, hsize, csize, ans = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
static void func(int idx, int cnt) {
if (cnt == M) {
int sum = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < hsize; i++) {
int dis = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
for (int j = 0; j < M; j++) {
int x = house[i][0] - pick[j][0];
int y = house[i][1] - pick[j][1];
dis = Math.min(dis, Math.abs(x) + Math.abs(y));
}
sum += dis;
}
ans = Math.min(ans, sum);
return;
}
for (int i = idx; i < csize; i++) {
pick[cnt][0] = chicken[i][0];
pick[cnt][1] = chicken[i][1];
func(i + 1, cnt + 1);
pick[cnt][0] = 0;
pick[cnt][1] = 0;
}
}
static void input() throws Exception {
st = new StringTokenizer(br.readLine());
N = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken());
M = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken());
list = new int[N][N];
house = new int[100][2];
chicken = new int[13][2];
pick = new int[13][2];
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) {
st = new StringTokenizer(br.readLine());
for (int j = 0; j < N; j++) {
list[i][j] = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken());
if (list[i][j] == 1) {
house[hsize][0] = i;
house[hsize++][1] = j;
} else if (list[i][j] == 2) {
chicken[csize][0] = i;
chicken[csize++][1] = j;
}
}
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
input();
func(0, 0);
System.out.println(ans);
}
}
|
cs |
'algorithm > Bruteforce' 카테고리의 다른 글
| boj 17281 ⚾ (0) | 2021.02.16 |
|---|---|
| boj 3040 백설 공주와 일곱 난쟁이 (0) | 2021.02.15 |
| boj 2961 도영이가 만든 맛있는 음식 (0) | 2021.02.15 |
| boj 2422 한윤정이 이탈리아에 가서 아이스크림을 사먹는데 (0) | 2021.01.29 |
| boj 1018 체스판 다시 칠하기 (0) | 2021.01.29 |